Output Variables
Introduction
Proggy command steps are designed to be executed sequentially.
For example, let’s say you have three steps:
- Ask user for server IP address
- SSH into server
- Run command on server
As you can see, your Prog asks the user for the IP address on Step 1. To execute Steps 2 and 3, we must be able to reference the IP address entered by the user.
In order for Steps 2 and 3 to reference the IP address inputted earlier, we can reference it using an Output Variable.
What is an Output Variable?
When you create a Command Step in Proggy, the system generates an unique identifier prefix. This prefix has the format of step[identifier].
Using the previous example, you might see the following:
- Ask user for server IP address (prefix of
step7f0968) - SSH into server (prefix of
step1268fc) - Run command on server (prefix of
step44f9fc)
With each prefix, you can use reference specific things about that particular step.
raw- Last output of the particular command stepdirective- Name of the directive executed on that stepposition- Position of the directive
For example, in the first step, it asks the user for the IP address of the server. The value that the user enters will be saved as step7f0968.raw. Therefore, in subsequent steps, you can reference the IP address using step7f0968.raw.
Piped variable
In addition to the prefix method of referencing values from specific steps, you can also use the prefix piped to reference the immediate preceding step.
For example, in Step 2, we can use piped.raw instead of step7f0968.raw. Both of these will reference the same thing.
Note, however, that when Prog begins executing Step 3, using piped.raw will reference Step 2 instead.
Custom name variables
Some directives have the option of explicitly naming its raw directive.
For example, the Ask User Input directive will prompt the user for an input. Instead of using the default step[identifier].raw reference, you can optionally specify the variable name:
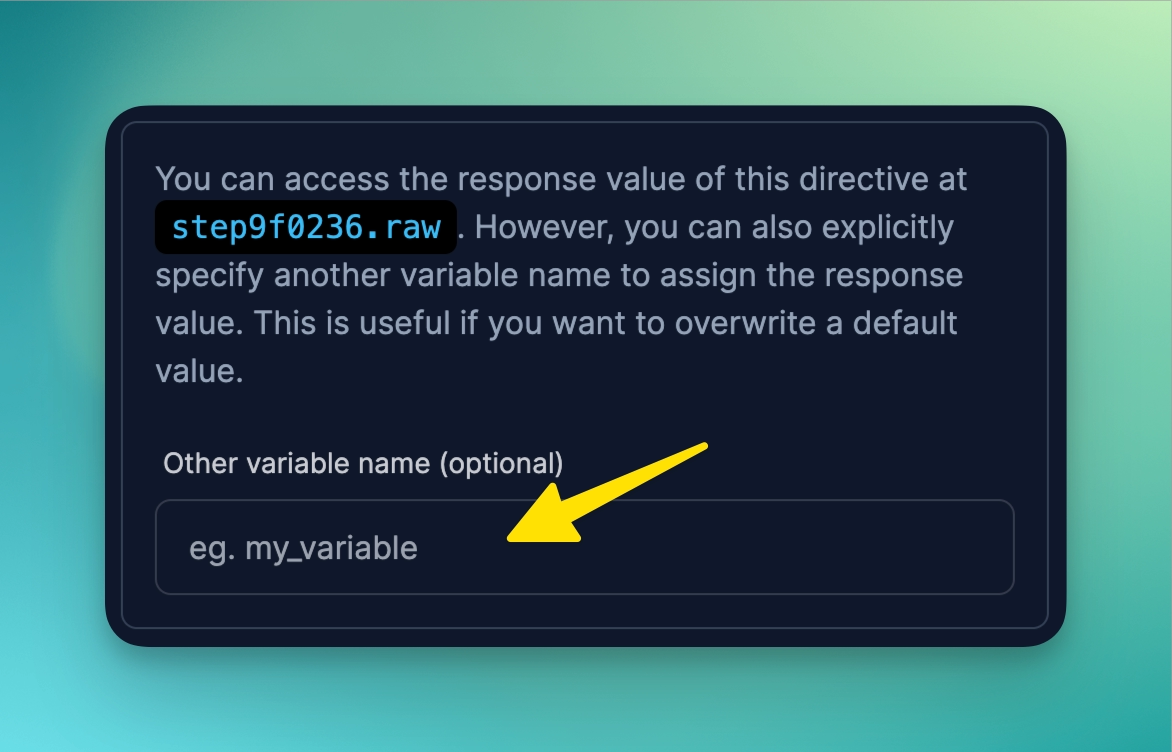
For example, let’s say you ask a user for a username, you can assign it the variable of username and then reference it as {{ username }}.
JSON output variables
Some directives make HTTP requests and can receive JSON formatted data responses:
In these cases, you can specify in your directive settings to parse the response (assuming you know it is in JSON format) and provide you with a “dot notation” access through a Liquid variable.
For instance, let’s say the response is this:
{
"status": "OK",
"message": "Hello World"
}
If the step directive has a prefix of step2fk9, you will be able to access the JSON response through step2fk9.json. Moreover, we can also access nested JSON data like so:
step2fk9.json.status => "OK"
step2fk9.json.message => "Hello World"
Warning when using output variables
Output variables are only available after the particular step is completed.
Here is a simple example:
- Your create a step which displays some text
- The step itself has a prefix of
step7f0968 - In the step, you want to output the step’s own position with
{{ step7f0968.position }}
If you set up the directive like this, the output of {{ step7f0968.position }} will be blank.
The reason for this is that the step, during its execution, has not yet populated the step7f0968 values.
Keep this in mind when constructing your Prog commands that output variables are only available after a step is completed.